The Center
for
Socratic
Principles:
The New
Whig
Party
Home
WhigCentral
The
NWP Quiz
The
American
Pageant Quiz
The
US Consitution, Bill of Rights, and the Amendments
Essays
The
NWP on
Yahoo!
The
Center's
Sponsors
A
News
Article I Liked
Send
us your
Comments





 |
Millard Fillmore
Fast Fact: Millard Fillmore's conciliatory politics helped
postpone the Civil War.
Biography: In his rise from a
log cabin to wealth and the White House, Millard Fillmore demonstrated
that through methodical industry and some competence an uninspiring man
could make the American dream come true.
Born in the Finger Lakes country of New York in 1800,
Fillmore as a youth endured the privations of frontier life. He worked
on his father's farm, and at 15 was apprenticed to a cloth dresser. He
attended one-room schools, and fell in love with the redheaded teacher,
Abigail Powers, who later became his wife.
In 1823 he was admitted to the
bar; seven years later he moved his law practice to Buffalo. As an associate
of the Whig politician Thurlow Weed, Fillmore held state office and for
eight years was a member of the House of Representatives. In 1848, while
Comptroller of New York, he was elected Vice President.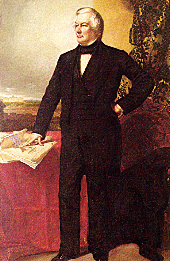
Fillmore presided over the Senate
during the months of nerve-wracking debates over the Compromise of 1850.
He made no public comment on the merits of the compromise proposals, but
a few days before President Taylor's death, he intimated to him that if
there should be a tie vote on Henry Clay's bill, he would vote in favor
of it.
Thus the sudden accession of Fillmore to the Presidency
in July 1850 brought an abrupt political shift in the administration. Taylor's
Cabinet resigned and President Fillmore at once appointed Daniel Webster
to be Secretary of State, thus proclaiming his alliance with the moderate
Whigs who favored the Compromise.
A bill to admit California still
aroused all the violent arguments for and against the extension of slavery,
without any progress toward settling the major issues.
Clay, exhausted, left Washington
to recuperate, throwing leadership upon Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois.
At this critical juncture, President Fillmore announced in favor of the
Compromise. On August 6, 1850, he sent a message to Congress recommending
that Texas be paid to abandon her claims to part of New Mexico.
This helped influence a critical number of northern Whigs
in Congress away from their insistence upon the Wilmot Proviso--the stipulation
that all land gained by the Mexican War must be closed to slavery.
Douglas's effective strategy
in Congress combined with Fillmore's pressure from the White House to give
impetus to the Compromise movement. Breaking up Clay's single legislative
package, Douglas presented five separate bills to the Senate:
1.Admit California as a free state.
2.Settle the Texas boundary and compensate
her.
3.Grant territorial status to New Mexico.
4.Place Federal officers at the disposal
of slaveholders seeking fugitives.
5.Abolish the slave trade in the District
of Columbia.
Each measure obtained a majority, and by September 20,
President Fillmore had signed them into law. Webster wrote, "I can now
sleep of nights."
Some of the more militant northern
Whigs remained irreconcilable, refusing to forgive Fillmore for having
signed the Fugitive Slave Act. They helped deprive him of the Presidential
nomination in 1852.
Within a few years it was apparent that although the
Compromise had been intended to settle the slavery controversy, it served
rather as an uneasy sectional truce.
As the Whig Party disintegrated
in the 1850's, Fillmore refused to join the Republican Party; but, instead,
in 1856 accepted the nomination for President of the Know Nothing, or American,
Party. Throughout the Civil War he opposed President Lincoln and during
Reconstruction supported President Johnson. He died in 1874.
Back
Courtesy of the White
House |
